Building a Master Data Operating Model for Large Government Entities
Large government entities manage vast datasets, citizen records, assets, suppliers, contracts, land registries, and compliance information. Without a structured master data operating model, this data gets trapped in silos, slows decision-making, and increases operational and regulatory risks.
A strong master data operating model creates unified standards, synchronized systems, and a single source of truth across ministries and departments. It gives leaders a clear framework to manage critical data consistently, reduce duplication, and support digital-government initiatives. This guide outlines the essential components of an effective operating model, the challenges governments must anticipate, and how CODA accelerates large-scale public-sector data transformation.
What Is a Master Data Operating Model?
A master data operating model is the blueprint that defines how master data is created, standardized, governed, approved, used, and maintained across an organization.
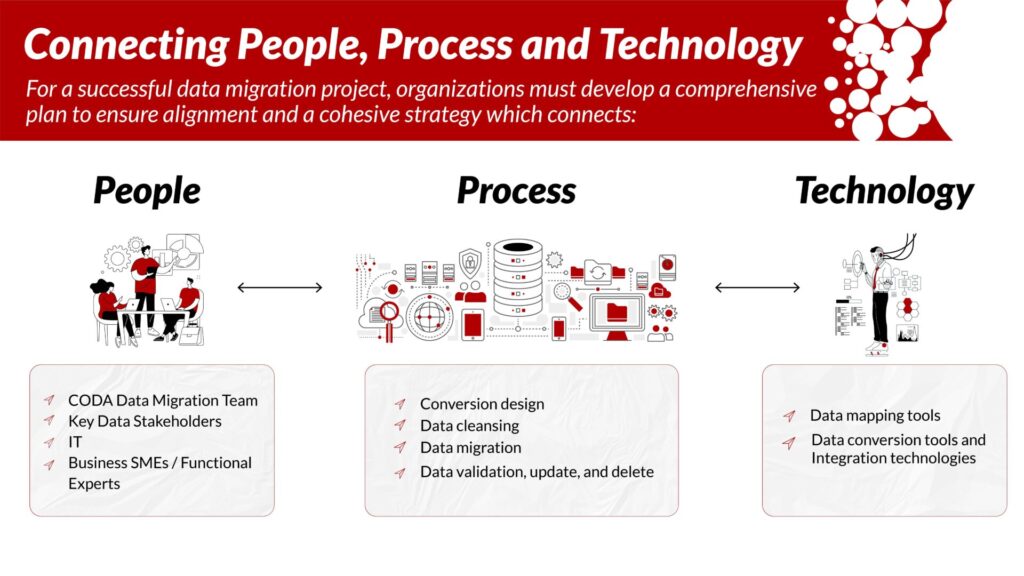
It connects people, processes, technology, governance, and data architecture into a unified system.
For government entities, this model covers domains like
- Citizen & resident records
- Assets & infrastructure
- Healthcare & social services data
- Licenses & permits
- Land & property records
- Contractors, suppliers & vendors
- Public safety & emergency response data
The purpose is simple: ensure everyone from the ministry to field teams works with clean, accurate, and consistent data.
Why Government Entities Need a Master Data Operating Model
Large public-sector organizations face challenges that private companies don’t. Departments often use different systems, follow different processes, and maintain their own versions of the same data and those inconsistencies lead to duplicate or conflicting records, delayed service delivery, inaccurate reporting, audit issues, compliance risks, and inefficiencies in procurement and budgeting
A master data operating model solves these problems by:
- Standardizing data definitions
- Eliminating duplicate records
- Enforcing workflows and approvals
- Ensuring every agency uses the same “golden record”
- Enabling analytics and real-time decision-making
- Improving transparency and accountability
For countries in the GCC, India, US, or the Far East undergoing digital transformation, this is now a foundational requirement, not an optional initiative.
Core Components of an Effective Operating Model for Governments
1. Governance & Ownership in a Master Data Operating Model
Master data governance gives you clear roles to ensure disciplined data management:
- Data Owners for each domain
- Data Stewards responsible for quality
- Governance Council for policy oversight
- Approval workflows for create/modify/delete requests
This ensures structure, accountability, and compliance across ministries and departments.
2. Data Standards & Modeling
Government datasets span many domains and formats, and without unified standards they become inconsistent and difficult to integrate. Differences in naming, coding, classification, and metadata create gaps in reporting, slow processes, and reduce reliability across departments.
A strong operating model establishes clear, enforceable rules for how master data is created and maintained, including:
- Standardized naming conventions
- Defined attribute requirements
- Hierarchical and relational structures
- Controlled metadata and taxonomies
- Alignment with industry and national standards
These elements form the core foundation for trusted, interoperable master data across the government ecosystem.
3. MDM Architecture & Technology
Government environments operate complex systems, so choosing the right MDM architecture is critical. Each style offers different levels of centralization and control, and the model must align with security needs, data sensitivity, and integration complexity.
Common MDM architectures include:
- Centralized: All master data governed and stored in one controlled hub
- Consolidation: Data aggregated and synchronized mainly for analytics
- Coexistence: Agencies maintain local systems but sync validated data to a central hub
- Registry: A master index links distributed systems without moving data
Selecting the right approach depends on scale, sensitivity, and the legacy system landscape.
4. Processes and Workflows for Effective Master Data Management
A strong operating model defines how master data is created, updated, validated, and retired. These workflows ensure consistency across ministries and reduce errors caused by manual or ungoverned practices. CODA automates these processes through rule-based workflows, multi-level approvals, and AI-driven validations, ensuring every master record enters the system clean, complete, and compliant.
Key workflows typically include:
- Asset registration and updates
- Data validation and multi-level approvals
- Scheduled audits and quality checks
- Merge and de-duplication procedures
- Data lifecycle and archival management
Clear processes ensure master data moves through the ecosystem in a controlled and compliant manner, with CODA enforcing standards at every step.

Streamline Your Master Data Workflows. Ensure every record follows policy-driven, automated processes.
5. Integration & Interoperability
Government platforms rarely come from the same vendor or technology era, yet they all need to talk to each other. A well-defined operating model makes the MDM platform the connective layer that keeps data flowing smoothly across every system.
And because CODASOL seamlessly integrates with SAP, Oracle, and IBM Maximo, and even offers PROSOL directly in the SAP Store, it fits right into existing government stacks without disrupting operations.
Typical integrations include:
- ERP platforms (SAP, Oracle, Maximo)
- eGovernment and citizen service portals
- Finance and budgeting systems
- Licensing and regulatory systems
- GIS and spatial data platforms
- HR and payroll applications
- Procurement and contract systems
APIs, real-time sync, and automated validations ensure every department stays aligned with the same trusted master data.
6. Data Quality, Compliance & Audit
Public-sector data is highly sensitive, ranging from citizen records to national assets, and requires strict controls. The operating model establishes the safeguards and quality standards needed to maintain accuracy and comply with regulations.
Core enforcement areas include:
- Defined data quality thresholds
- End-to-end audit trails
- Security and role-based access control
- Regulatory and policy compliance
- Versioning and change history tracking
These measures support transparency, accountability, and trust across government operations.
A Practical Roadmap to Build the Operating Model
Step 1: Understand the Current Data Environment
The first step is assessing all systems and datasets across departments to identify gaps, duplicates, and inconsistencies. Advanced MDM platforms, like Coda, can automatically map data sources and highlight quality issues, giving government teams a clear view of their current data landscape and readiness for structured management.
Step 2: Define Governance within the Master Data Operating Model
Clear governance is essential for a successful operating model. Organizations can assign domain owners, define steward responsibilities, and implement approval workflows while embedding policies and standards into day-to-day operations. This ensures accountability and reduces errors across ministries and departments.
Step 3: Select the Most Suitable MDM Architecture
Choosing the right architecture depends on multiple factors, including the number of agencies involved, the sensitivity of the data, the existing IT ecosystem, public service requirements, and reporting and analytics objectives. The architecture sets the foundation for centralized control, coexistence, consolidation, or registry-based approaches.
Step 4: Build Data Standards and Quality Rules for the Operating Model
After defining the architecture, establishing data standards and quality rules is critical. Tools for normalization, validation, and taxonomy creation combined with Data Cleansing and Enrichment ensure that master data is accurate, consistent, and interoperable across all government systems.”
Step 5: Pilot the Master Data Operating Model
Implementation begins with a high-impact pilot domain such as suppliers, citizens, assets, or land records. Pilots demonstrate early results by streamlining approvals, classification, and data cleansing, generating tangible value while mitigating risks before full-scale adoption.
Step 6: Scale the Master Data Operating Model Across Government
Following a successful pilot, the operating model can be extended across additional domains and systems. Seamless integration with ERPs like SAP, Oracle, and Maximo, along with automated workflows and governance enforcement, ensures consistent and trusted master data throughout the government ecosystem.
Step 7: Monitor Performance Through Key Metrics
Ongoing measurement is key to sustaining the model. Tracking metrics such as duplicate reduction, data accuracy, approval cycle times, compliance scores, and cross-agency usage helps maintain high-quality master data, improve operational efficiency, and refine governance practices over time.

Strengthen your government’s data foundation with expert-designed MDM workflows.
How CODA Supports the Master Data Operating Model for Large Government Entities
CODA, CODASOL’s AI-driven Master Data Management platform, is built for national-scale, multi-agency environments. Its architecture and features directly support each pillar of a government-ready operating model.
1. AI-Driven Data Quality & Automation
CODA uses machine learning to automate:
- Duplicate detection
- Attribute prediction
- Code generation
- Smart metadata suggestions
- Classification and standardization
- Rule-based validations
This reduces manual effort across ministries and improves accuracy.
2. Strong Governance & Controlled Workflows
CODA provides:
- Domain-level ownership
- Approval chains
- Audit logging
- User access controls
- Policy enforcement
This brings consistency across all government entities using the platform.
3. Seamless Integrations with Government Systems
CODA integrates with:
- SAP
- Oracle EBS
- Maximo
- National e-services
- GIS systems
- Legacy databases
- Custom government applications
This supports cross-agency workflows and real-time synchronization.
4. Government-Scale Security & Compliance
CODA offers:
- Full audit history
- Role-based data visibility
- Encryption of sensitive fields
- Integration monitoring
- Compliance-ready governance
These features make it suitable for ministries, utilities, ports, smart city programs, and regulatory bodies.
5. Proven Track Record in Government & Public Sector
CODASOL has executed MDM and governance programs for:
- GCC ministries
- National oil companies
- Port and maritime authorities
- Municipalities
- Public utilities
- Industrial government-linked enterprises
This experience ensures government teams receive expert, domain-specific implementation support.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do government entities need a Master Data Operating Model?
It eliminates duplicate records, improves service delivery, strengthens compliance, and ensures consistency across all government systems.
2. Which MDM architecture is best for governments?
Centralized and coexistence models are most common due to high compliance needs and cross-agency coordination.
3. How long does it take to build a MDM operating model?
Pilots take a few weeks, while full deployment can take several months depending on agency size and complexity.
4. How does CODA support multi-agency data governance?
CODA enforces workflows, automates quality checks, integrates with existing systems, and supports domain-specific standards.
5. What are the most important KPIs for success?
Data accuracy, duplicate reduction, approval cycle time, audit improvements, and cross-agency data usage.
Modernize your master data foundation with CODA’s AI-enabled platform.

