E-SPIR & Spare Parts Review: How to Run a Fast, Accurate Spare Parts Audit
A spare parts audit is essential for asset-intensive industries struggling with unreliable spare parts data, one of the most common and costly operational problems. Duplicate materials, incorrect specifications, missing interchangeability details, and uncontrolled part creation silently inflate inventory, delay maintenance, and increase downtime.
A structured spare parts audit, supported by E-SPIR (Electronic Spare Parts Interchangeability Records) and governed through Master Data Management (MDM), is the fastest and most reliable way to restore accuracy, control, and confidence in spare parts operations.
This guide explains how to run a fast, accurate spare parts audit, why E-SPIR is critical, how MDM sustains audit outcomes, and how organizations across Oil & Gas, Manufacturing, Energy & Utilities, and Pharmaceuticals can build a future-ready spare parts foundation.
What Is a Spare Parts Audit, and How Does an E-SPIR Review Work?
A spare parts audit is a structured review of spare parts master data to ensure that every part record is technically correct, non-duplicative, properly classified, and aligned with operational needs.
An E-SPIR (Electronic Spare Parts Interchangeability Record) is a digital record that documents approved spare parts and their interchangeable or equivalent alternatives. It ensures maintenance and procurement teams select the right part without delays, rework, or risk.
Together, spare parts audits and E-SPIR reviews help organizations:
- Eliminate duplicate and obsolete spare parts
- Improve maintenance response time
- Reduce excess inventory and emergency purchases
- Create a single source of truth for spare parts data
Why Spare Parts Audits Matter in Asset-Intensive Industries
Oil & Gas
Unplanned downtime in Oil & Gas operations can cost millions per hour. Inaccurate spare parts data leads to delayed repairs, incorrect part procurement, and excessive safety stock.
Manufacturing
Production lines depend on the timely availability of the right spares. Poor data results in line stoppages, overstocked slow-moving inventory, and fragmented visibility across plants.
Energy & Utilities
Utilities rely on critical spares to ensure uninterrupted service. Regulatory scrutiny also demands traceable, accurate spare parts records.

Facing the same spare parts challenges?
See how CODASOL Industry Solutions help.
Pharmaceuticals
Compliance and equipment reliability are non-negotiable. Incorrect spare parts data can lead to failed audits, batch losses, and extended equipment downtime.
A spare parts audit directly addresses these risks by aligning engineering, maintenance, procurement, and inventory teams around accurate, governed data.
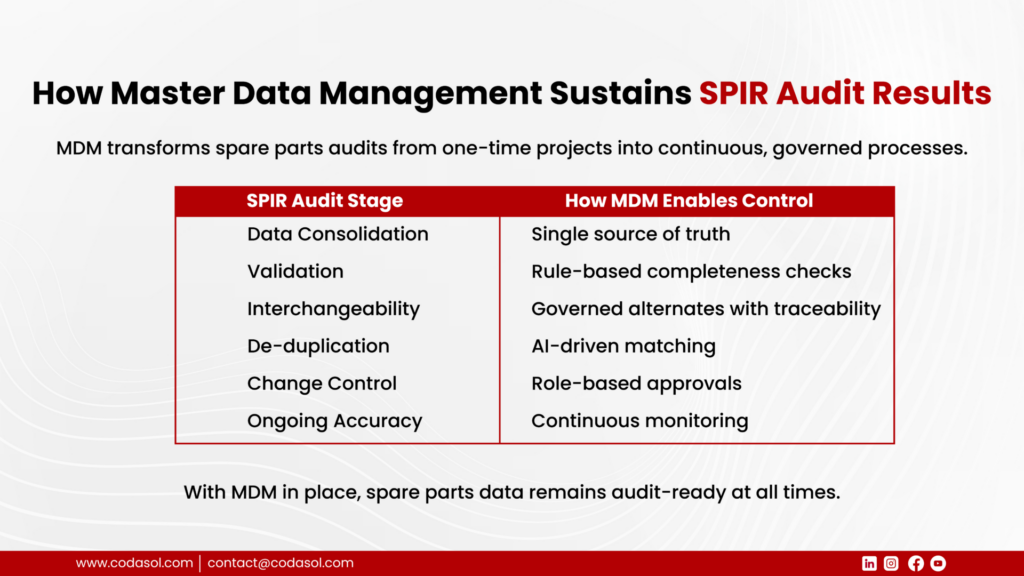
The Complete Spare Parts Audit Framework (MDM-Led Approach)
Step 1: Define Scope and Criticality for the Spare Parts Audit
Start by identifying:
- Critical assets and equipment
- High-risk and long-lead-time spares
- Safety- and compliance-related parts
This ensures the audit focuses on what matters most to operations.
Step 2: Consolidate Spare Parts Data for an Accurate Spare Parts Audit
Spare parts data often exists across:
- ERP systems (SAP, Oracle)
- CMMS/EAM platforms (Maximo)
- Legacy spreadsheets and vendor catalogs
MDM enables consolidation by creating a single, governed master record for each spare part across all systems.
Step 3: Validate Technical Accuracy
Each spare part record is validated for:
- OEM part numbers
- Technical specifications
- Materials and ratings
- Drawings and document references
MDM enforces mandatory attributes and validation rules, preventing incomplete or incorrect records from entering the system.
Step 4: Review Interchangeability Using E-SPIR
E-SPIR reviews ensure that:
- Approved alternate parts are identified
- Functional equivalence is validated
- Engineering approvals are documented
This reduces dependency on single suppliers and accelerates maintenance execution.
MDM governs interchangeability records, ensuring full traceability and controlled approvals.
Step 5: Identify and Eliminate Duplicates
Duplicates typically arise from:
- Free-text descriptions
- Vendor-specific part creation
- Lack of standard naming conventions
MDM uses AI-assisted matching and standardization to identify and eliminate duplicates while preventing their re-creation post-audit.

Still struggling with duplicate spares and unreliable spare parts data?
Step 6: Classify, Rationalize, and Optimize Inventory
Spare parts are classified based on:
- Criticality
- Usage and consumption
- Obsolescence risk
This supports inventory optimization, min–max planning, and demand forecasting.
E-SPIR & Spare Parts Audit Checklist
| Audit Area | Key Validation Points |
|---|---|
| Part Description | Standardized, no free text |
| OEM & Specifications | Verified and complete |
| Interchangeability | Approved and documented |
| Duplication | Functional and technical checks |
| Classification | Criticality and usage defined |
| Governance | Approval workflows enforced |
Why Spare Parts Audits Fail Without MDM
Many organizations complete spare parts audits only to face the same issues within months.
Common reasons include:
- No control over new part creation
- Multiple data owners across systems
- Manual approvals without validation
- Inconsistent standards
- Gradual data decay
Without MDM, spare parts audits become repeated clean-up exercises instead of long-term solutions.
How CODASOL Delivers MDM-Led Spare Parts Audits and SPIR Reviews
CODASOL approaches every spare parts audit as part of a broader master data transformation strategy, not a one-time clean-up exercise. The objective is not only to correct spare parts data but to ensure it remains accurate, governed, and audit-ready across its lifecycle.
At the core of this approach is PROSOL, CODASOL’s enterprise-grade Master Data Management platform, purpose-built to handle complex spare parts data at scale.
CODASOL’s SPIR & Spare Parts Audit Approach
End-to-End Spare Parts Audit and E-SPIR Review
CODASOL conducts comprehensive spare parts audits covering data extraction, validation, rationalization, and E-SPIR review. PROSOL consolidates spare parts data from ERP, CMMS, and legacy systems into a single, governed master record, creating a reliable single source of truth.
Engineering-Led Validation of Specifications and Interchangeability
Spare parts specifications, OEM references, and interchangeability details are validated by engineering experts. PROSOL captures approved alternates and interchangeability relationships with full traceability, ensuring maintenance teams can confidently select equivalent parts without operational risk.
AI-Driven De-duplication and Normalization
Using AI-assisted matching and rule-based standardization, PROSOL identifies functional and technical duplicates across large spare parts catalogs. Once cleansed, governance controls prevent duplicate spare parts from being recreated after the audit.
ERP and CMMS Integration with SAP, Oracle, and Maximo
PROSOL seamlessly integrates with leading ERP and CMMS platforms, ensuring that cleansed and governed spare parts data flows consistently across procurement, maintenance, and inventory systems. This eliminates discrepancies between operational and master data environments.
Continuous Data Governance Using MDM
Beyond the audit, PROSOL enforces role-based approvals, validation rules, and change management workflows. Every new or updated spare part record is governed, ensuring long-term data quality and sustained audit readiness.
By combining deep SPIR expertise with the PROSOL MDM platform, CODASOL ensures spare parts data remains accurate, standardized, and reliable long after the spare parts audit is complete.
Business Outcomes of an MDM-Driven Spare Parts Audit
Organizations that adopt MDM-led spare parts audits typically achieve:
- Reduced inventory carrying costs
- Faster maintenance turnaround times
- Improved procurement accuracy
- Lower operational risk
- Continuous audit readiness
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a spare parts audit?
A spare parts audit is a structured review of spare parts data to validate accuracy, duplication, classification, and interchangeability.
2. What is E-SPIR used for?
E-SPIR documents approved spare parts and interchangeable alternatives in a controlled, digital format.
3. Why is MDM important for SPIR audits?
MDM prevents data decay by enforcing standards, approvals, and governance across the spare parts lifecycle.
4. How often should spare parts audits be conducted?
An initial audit should be followed by continuous governance using MDM rather than repeated full-scale audits.
5. Can spare parts audits integrate with SAP or Maximo?
Yes. MDM enables seamless integration with ERP and CMMS platforms such as SAP, Oracle, and Maximo.
Final Wrap
A spare parts audit is no longer just a maintenance task; it is a strategic data initiative. When powered by E-SPIR and governed through MDM, organizations move beyond one-time data cleanup to sustained control over spare parts creation, procurement, and maintenance execution.
An MDM-led approach ensures spare parts data remains accurate, audit-ready, and reliable, transforming it from a recurring operational risk into a long-term business asset.
Ready to eliminate duplicate spares, improve maintenance reliability, and govern spare parts data at scale?

