In the evolving industrial landscape, standardizing material codes has emerged as a mission-critical process for sectors like Oil & Gas, Utilities, Manufacturing, Real Estate & Construction, Marine & Ports, Healthcare & Lifesciences, and EPC companies. With the rise of ERP systems and AI-driven data management tools, businesses across regions, including India, the GCC, the Far East, and the US, are recognizing the strategic value of accurate, clean, and standardized material master data.
Why Material Code Standardization Matters
In complex, asset-intensive industries, materials are the backbone of procurement, maintenance, and operations. However, disparate naming conventions, inconsistent abbreviations, and duplicated entries often plague master data. This leads to:
- Overstocking or stockouts
- Inefficient procurement cycles
- Wasted operational hours
- Difficulty in digital transformation or ERP migrations
Standardizing material codes helps businesses establish a single source of truth, enabling efficient decision-making, optimized inventory, and cost savings.
Common Issues vs. Benefits of Material Code Standardization
| Common Issues | Standardization Benefits |
|---|---|
| Duplicate material entries | Accurate inventory visibility |
| Inconsistent naming conventions | Easier material search and cataloging |
| Non-compliant codes with ERP standards | Seamless ERP integration (SAP, Oracle, Maximo) |
| Excessive manual intervention | Automated classification and faster procurement |
| Poor reporting and analytics | Better business intelligence and predictive planning |
Best Practices for Standardizing Material Codes
1. Develop a Unified Material Coding Taxonomy
Create a standard structure for all material codes across business units and geographies. This includes:
- Hierarchical coding (Category – Subcategory – Item)
- Consistent field length and delimiter rules
- Use of international classification systems (e.g., UNSPSC, eCl@ss)
Example: “PIP-FLG-CARB-150MM” could represent a carbon steel flange used in piping applications.
2. Leverage AI/ML for Auto-Classification and Cleansing
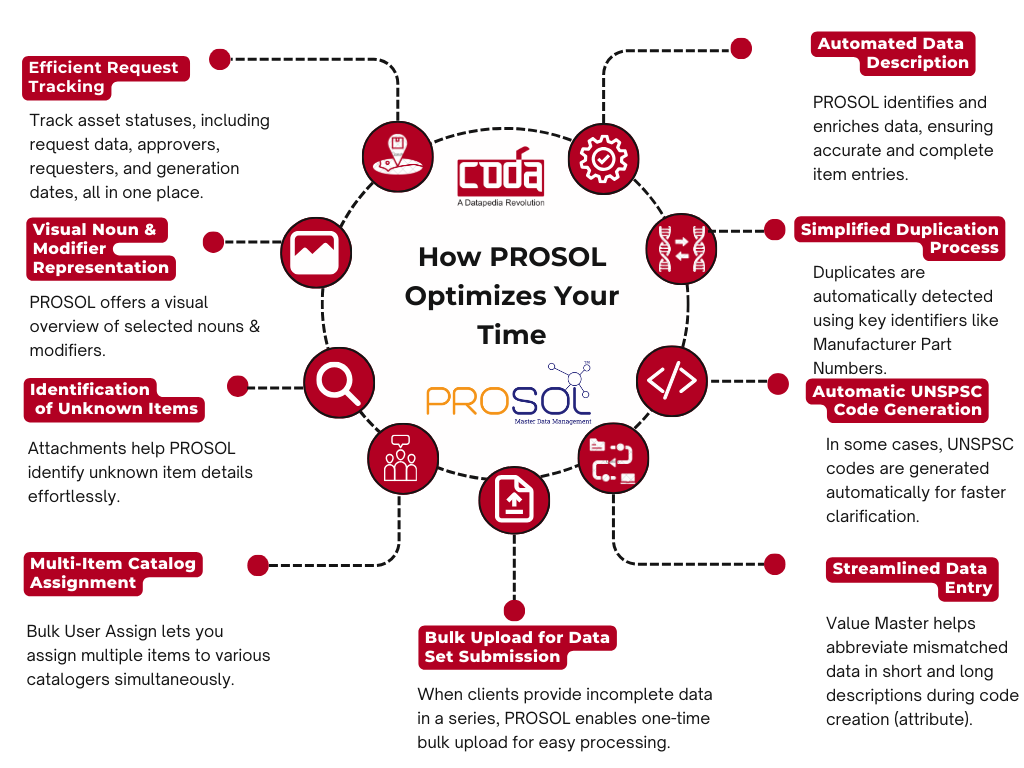
Modern Master Data Management (MDM) platforms like CODASOL’s PROSOL leverage AI/ML to:
- Detect duplicates
- Auto-classify based on specifications
- Recommend standard descriptions
- Enrich data using external references or manufacturer catalogs
This helps scale material code standardization across thousands of SKUs.
3. Involve Cross-Functional Stakeholders
Material data is not just an IT responsibility. Collaborate with:
- Procurement teams (to understand purchase patterns)
- Maintenance engineers (to validate technical specs)
- Finance (to align with asset valuation)
Cross-functional input ensures the codes are usable, not just standardized.
4. Map Material Codes to ERP Systems
Ensure material codes align with your ERP system’s logic. For example:
- SAP supports 18-character material codes
- Oracle may allow alphanumeric with special characters
Use mapping templates during ERP migration or integration to avoid data loss or rework.
5. Ensure Regional & Compliance-Based Customizations
For industries operating across India, GCC, Far East, and the US, localization matters:
- Align with regional taxonomies and procurement standards
- Respect language preferences and unit conventions
- Maintain dual codes for global vs. local operations, if needed
6. Governance Through a Material Master Data Policy
Implement a governance model that includes:
- Approval workflows for new material creation
- Defined roles and responsibilities (data stewards, approvers)
- Continuous audits and exception reporting
Use MDM platforms to enforce governance with built-in workflows and dashboards.
7. Standardize Descriptions for Searchability
Poorly written material descriptions can cripple procurement operations. Use these tips:
- Avoid abbreviations unless standardized
- Start with noun, followed by qualifiers (e.g., “Valve, Gate, SS304”)
- Follow format: [Noun] – [Type] – [Material] – [Size] – [Specs]
Use controlled vocabularies and catalogs for consistency across teams.

Want to Eliminate Duplicate Materials and Save Costs?
Our material master audit can reveal up to 20% redundancies in your inventory.
8. Deduplicate and Rationalize Inventory
Many organizations carry 12–20% redundant material records, leading to excess holding costs.
- Use de-duplication tools to identify similar or identical items
- Consolidate items with minor variations
- Rationalize by removing inactive or obsolete SKUs
This can save millions annually, especially in sectors like Oil & Gas and EPC.
9. Train Teams on Standards and Tools
Tool adoption fails if teams don’t understand the “why” and “how.” Invest in:
- Workshops on naming conventions
- Training on MDM platforms
- Periodic refreshers on governance policies
Make standardization part of your organizational culture.
10. Measure Impact and Iterate
Track KPIs like:
- % Duplicate Reduction
- Inventory Value Saved
- Material Creation Cycle Time
- ERP Integration Success Rate
Review these KPIs quarterly and refine standards as needed.
Case Study:
How a Global Healthcare Leader Standardized 100K+ Material Codes
A leading multinational healthcare manufacturer with facilities in India, the US, and Brazil faced significant master data challenges, ranging from duplicate spare parts to inconsistent naming conventions. Operating in regulated markets like the US, Europe, and South Africa, they needed a robust solution that ensured compliance, efficiency, and standardization across plants.
Their Key Challenges
- Difficulty distinguishing chemical compounds, impurities, and reference standards
- High volume of duplicate spare item entries
- Frequent delays in material code creation and updates
- Inconsistent UOMs and UNSPSC codes impacting procurement
CODASOL’s Solution via PROSOL
Using our AI-powered MDM platform, PROSOL, we implemented a streamlined, SLA-driven process:
- Validated and corrected material types, UOMs, and groups
- Performed 100% duplicate checks on new requests
- Reviewed and updated UNSPSC classifications
- Executed urgent updates, even on holidays, to avoid business disruption
- Blocked outdated materials and amended codes in real-time
- Provided ongoing support for audit rectifications and user training
The Result
- 3-day SLA achieved for all requests
- Full compliance with naming conventions and audit standards
- Enhanced procurement accuracy and reduced material redundancy
- Empowered plant users through continuous knowledge transfer
Frequently Asked Questions:
1: How often should material codes be reviewed or updated?
Best practice is to audit the material master every 6–12 months, especially after ERP upgrades or M&A activity.
2: Can AI tools fully automate material code standardization?
AI/ML can handle classification and duplication to a large extent, but human validation is essential for accuracy and compliance.
3: What’s the ideal length for a material code in ERP systems?
Depends on the system; SAP supports 18 characters, while others may vary. The key is consistency within the organization.
4: Are global standards like UNSPSC necessary?
While not mandatory, aligning with global standards enhances compatibility, especially for multinationals operating across regions.
5: How much can companies save through material code standardization?
Savings range from 5–15% of inventory value, primarily through reduced duplication, optimized procurement, and fewer stockouts.
Struggling with ERP Integration Due to Poor Data?
See how PROSOL can auto-classify and cleanse 100,000+ material records in just weeks.


